Human subjects
The Stanford Institutional Review Board approved this trial, which was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04196413). Informed patient or parent consent and child assent were obtained. Included in consent is permission to share the (deidentified) results of the trial in scientific publications or presentations. Permission to publish images, photographs and videos was also obtained.
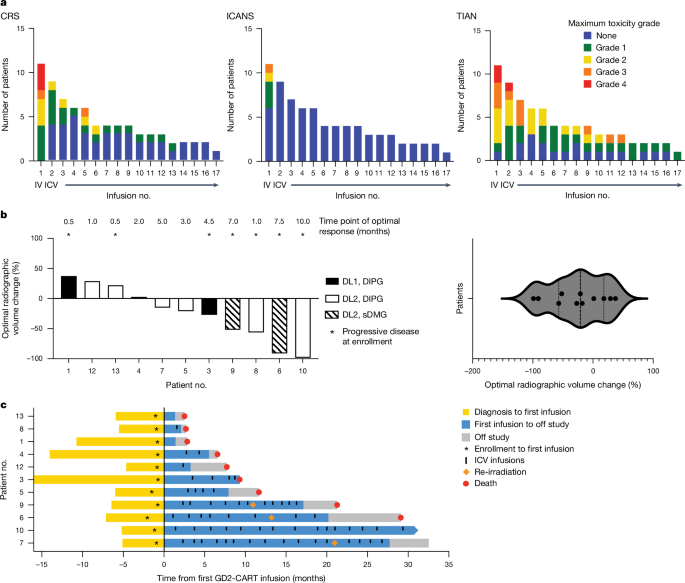
Response assessment
Clinical response was assessed using the CIS3 generated by protocol-directed neurological examinations performed by a neuro-oncologist at prescribed times following GD2-CAR Tâcell administration. The CIS represents a simple quantification of the neurological examination, which added or subtracted one point for each symptom/sign that improved or worsened, respectively, from the patientâs preinfusion baseline examination (Supplementary Methods 5). For patients who received corticosteroid therapy for toxicity management, CIS scoring was deferred until at least 7âdays following corticosteroid discontinuation. Imaging responses were assessed by MRI scans of the brain and/or spinal cord with and without gadolinium. Because DMGs are diffusely infiltrative of CNS structures and difficult to measure in linear dimensions, volumetric segmentation of tumour corresponding to abnormal T2 signal was performed by a neuroradiologist to measure radiographic change in tumour volume, consistent with RANOâ2.0 recommendations41.
Statistical analysis
Sample size estimation was based on clinical considerations and the PhaseâI 3â+â3 design. The targeted DLT rate was 30% or less. All patients who enroled into armâA and received one infusion of GD2-CAR Tâcells on trial were included in the analysis. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize baseline patient and disease characteristics, toxicity data and correlative and clinical outcomes. The ShapiroâWilk test of normality was used to assess normal (Gaussian) distribution of tumour volumetric response data. Overall survival was measured from date of diagnosis to the date that event occurred, or censored at the time of data cut-off. Survival probability was estimated using the KaplanâMeier method42. The confidence interval of median survival time was constructed by the method of BrookmeyerâCrowley43. All comparisons made in correlative outcomes were exploratory. MannâWhitney U-test was used, with no adjustments made for multiple comparisons. Statistical analyses were conducted using Prism software.
Correlative studies
Peripheral blood and CSF samples were collected before and following IV and ICV infusions to measure cytokine/chemokine levels in blood and CSF, GD2-CART persistence by qPCR and CAR-FACS and cell-free tumour DNA in CSF, as detailed in the previous report of the first four patients3 and reiterated below.
qPCR measurement of in vivo GD2-CAR expansion
Patient blood samples were processed and mononuclear cells viably cryopreserved. DNA was extracted from whole blood (2âÃâ106â5âÃâ106 peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)) using the QIAmp DNA blood Mini Kit (Qiagen, catalogue no. 51306) at baseline and at multiple time points following CAR administration. CAR presence was measured by qPCR using the primer and probe sequences provided below. For the standard curve, a custom Minigene plasmid (IDT) was designed containing a partial GD2.41BB.z sequence and a partial albumin sequence, which served as a control for normalization. The standard curve contained a tenfold serial dilution of plasmid ranging between 5âÃâ108 and 5âÃâ100 copies. Both plasmid and patient DNA from each time point were run in triplicate, with each reaction containing 5âµl of DNA (50âng total), 200ânM forward and reverse albumin primers (or 300ânM forward and reverse GD2.41BB.z primers), 150ânM probe suspended in 10âµl of TaqMan Fast Universal PCR Master Mix (2X), no AmpErase UNG (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and either 24.5âµl (albumin) or 22.5âµl (GD2.41BB.z) of TE buffer (Invitrogen, catalogue no. AM9935). The Thermo Fisher Scientific QuantStudioâ6 Pro Real-time qPCR Instrument was used for qPCR, with 20âµl per reaction. Quality metrics for all qPCR standard curve results were R2â>â0.95 and efficiency 70â110%.
Albumin results from the plate were normalized to average albumin, then GD2-CAR copy number (copies per 50âng of DNA), adjusted to albumin and modified to copies per 100âng of DNA, was calculated by the following equation: copy number (copies per 100âng of DNA)â=â2âÃâ(GD2-CAR copy numberâÃâ(albumin copy number/average albumin)).
Real-time flow cytometry assay
A high-dimensional, immunophenotyping, flow cytometry panel was designed for immune profiling of CAR Tâcells in real time. PBMCs were isolated from fresh whole blood by gradient centrifugation on ficoll (Ficoll paque Plus, GE Healthcare, Sigma-Aldrich). Between 2âmillion and 5âmillion PBMCs were stained with fixable Live/Dead aqua (Invitrogen) amine-reactive viability stain. Cells were preincubated with Fc block (trustain, BioLegend) for 5âmin, then stained at room temperature with fluorochrome-conjugated mAb in a 15-colour, 17-parameter staining combination as previously described3. Antibodyâfluorochrome conjugates used were: anti-CD3-FITC (BioLegend, 0.5âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD8-PerCP Cy5.5 (BD Biosciences, 0.5âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD45-BV785 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anto-CD4-BV711 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD95-BV650 (BioLegend, 0.5âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); CD39-BV605 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD57-BV421 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CCR7-BUV805 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD45RA-Alx700 (BioLegend, 0.5âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-GD2-CAR-DyLight650 (custom, cloneâ1A7, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD14-PE-Cy7 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD11b-APC-Cy7 (BioLegend, 1âµg of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); anti-CD33-PE-Dazzle (BioLegend, 5âµl of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl); and anti-GD2-PE (BioLegend, 5âµl of antibody per 1âmillion cells in 100âµl). For determination of the optimal concentration of antibody for staining in the CAR-FACS panel, each fluorochrome-conjugated antibody was titrated to determine the saturating amount of antibody needed to stain a test of 1âmillion cells. Doseâresponse curves for each antibody informed the saturating amount of fluorochrome-conjugated antibody required for staining 1âmillion cells in 100âml of staining volume.
CAR-tranduced Tâcells were used as positive control included in daily staining experiments. Immunostained and fixed cells were acquired on an LSR (BD BioSciences) five-laser (blue, 488ânm; violet, 405ânm; ultraviolet, 355ânm; red, 640ânm; green, 532ânm) analyser. A minimum of 106âcells were acquired, unless restricted by the number of cells isolated from 8âml of whole blood or when acquiring isolated cells from CSF. The assay limit of detection for cells was calculated as 1 in 104 of total acquired PBMCs. Representative gating is shown in Extended Data Fig. 10.
Luminex cytokines
Patient blood and CSF samples were collected at predetermined and trigger time points throughout treatment. Samples were spun at 250g for 6âmin. Supernatant was frozen at â80â°C until batched for assessment. Cytokine assessment was performed with the Immunoassay Team-Human Immune Monitoring Center at Stanford University. Panels include LuminexâEMD Millipore HIMC H80 (panelâ1 is Milliplex HCYTA-60K-PX48; panelâ2 is Milliplex HCP2MAG-62K-PX23; panelâ3 includes Milliplex HSP1MAG-63K-06 and HADCYMAG-61K-03 (resistin, leptin and hepatocyte growth factor) to generate a nine-plex) and TGF-b (TGFBMAG-64K-03). Kits were purchased from EMD Millipore and used according to the manufacturerâs recommendations, with modifications described. The assay set-up followed the recommended protocol. Briefly, samples were diluted threefold for panels 1 and 2 and tenfold for panelâ3. Diluted sample (25âµl) was mixed with antibody-linked magnetic beads in a 96-well plate and incubated overnight at 4â°C with shaking. Both cold and room-temperature incubation steps were performed on an orbital shaker at 500â600ârpm. Plates were washed twice with wash buffer in a Biotek ELx405 washer (BioTek Instruments). Following incubation for 1âh at room temperature with biotinylated detection antibody, streptavidin-PE was added for 30âmin with shaking. Plates were washed as described above, and PBS added to wells for reading in the Luminex FlexMap3D Instrument with a lower bound of 50âbeads per sample per cytokine. Custom Assay Chex control beads (Radix Biosolutions) were purchased and added to all wells. Wells with a bead count under 50 were flagged, and data with a bead count under 20 were excluded. Data are presented as picograms per millilitre, based on standard curves or heat maps of fold change from the baseline time point. All samples were run in technical duplicate.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.